3. PPI in the Research Cycle
Here are some examples of PPI at different stages of the research cycle.
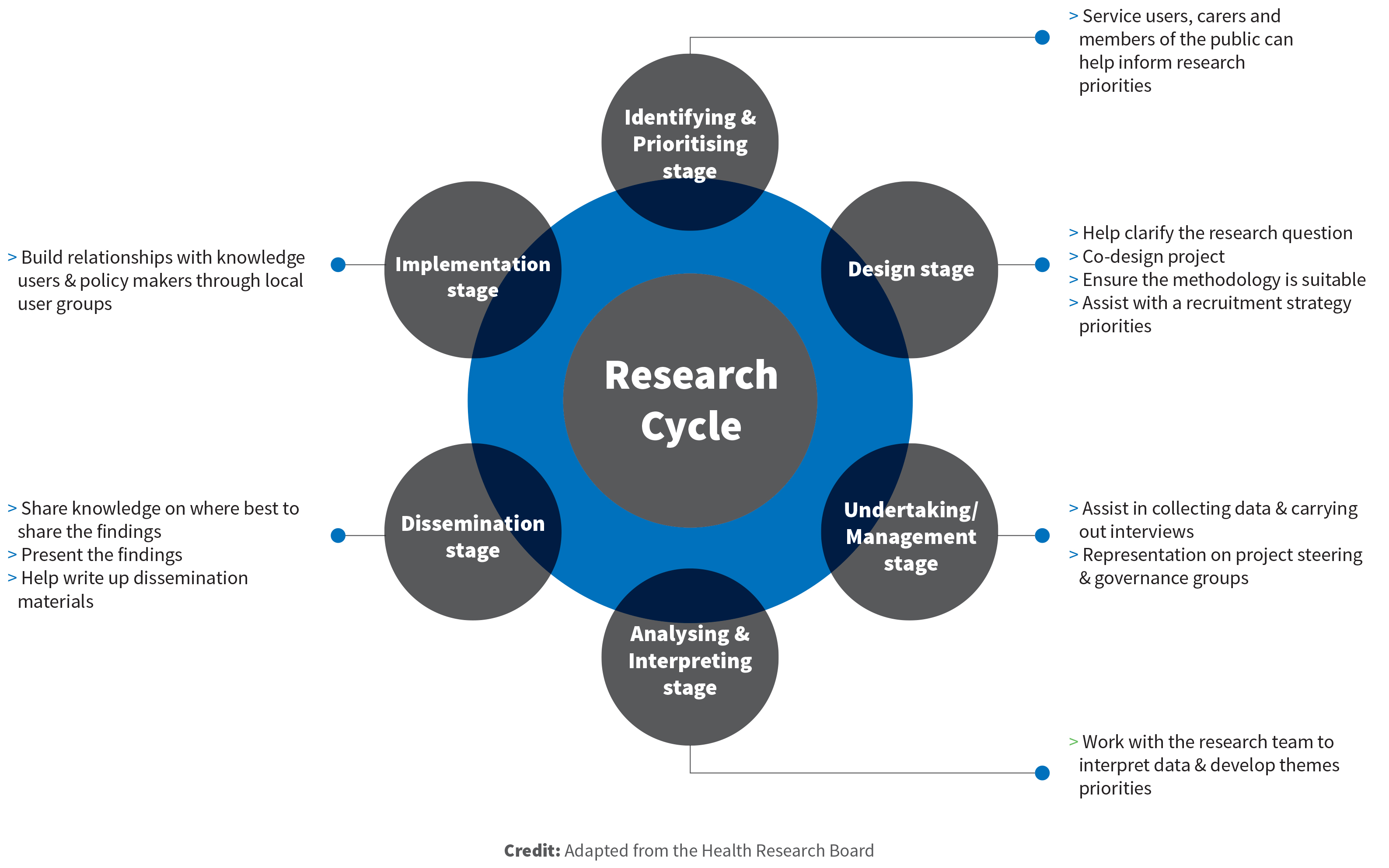
Source: HRB website
When viewing a research cycle like this, a question often occurs for researchers who would struggle certain aspects of the activities suggested. For example, a lab-based researcher might not easily be able to incorporate PPI contributors into the Analysis stage or that the methodology is appropriate at Design stage. These issues are mirrored by PPI contributors who do not want 'tokenistic' involvement, where they have no say and their perspective is irrelevant to the discussion.
Always consider, honestly, where a PPI contributor can have a meaningful input or where useful conversations can be had that will benefit the research cycle. Where that is not the case, or is not building towards that, you must consider whether you are wasting your own and other people's time.

